|

Saxon viking axe | Anglo Saxon History |  | |
| | Roman Ironworking in the weald and why it declined |
|---|
| | |
|---|
Classis Britannica - Background ▲
|
|---|
From Wikipedia
'The Classis Britannica (literally, British fleet, in the sense of 'the fleet in British waters' or 'the fleet of
the province of Britannia', rather than 'the fleet of the state of Britain') was a provincial naval fleet of the navy of
ancient Rome. Its purpose was to control the English Channel and the waters around the Roman province of Britannia.
Unlike modern (and some contemporary Roman) "fighting navies", its job was largely the logistical movement of personnel
and support, and keeping open communication routes across the Channel.'
A fleet was originally raised for the invasion of Britain under Claudius, with the task of bringing an invasion
force of 40,000 men from the Roman army, plus supplies, to Great Britain. It continued after the successful invasion to
provide support for the army, shuttling massive quantities of supplies across the English Channel.
Its original purpose was for transport, and as such had limited fighting vessels, it would seem that the fleet was
responsible for the industrialisation of the iron working in the Weald due to the number of tiles found in the area
marked CLBR.
It would seem that production knowledge improved significantly over the centuries as small bloomeries were
superceeded by much larger production sites such as Beauport Park, Oaklands and Footlands near Battle and Bardown near
Stonegate.
| | Reason for the Roman Invasion of Britannia ▲ |
|---|
The supply of iron from the Kent and Sussex coasts into Gaul by the Celts was probably one of the main reasons that
Britannia was invaded, to ensure that this supply of iron, needed in quantity by the Legions for armour and weapons, was
controlled by Rome.
| | Classis Britannica - Operations and Evidence ▲ |
|---|
Documentary evidence
There are no documents referring to 'Classis Britannica' but the name can be inferred from the other Roman fleet
names plus numerous tiles and bricks found around the South Coast in Kent and East Sussex stamped 'CLBR'.
Iron production and logistics
The fleet appears to have been an intrinsic part of the Roman period Wealden Iron industry, evidenced by the stamped
tiles found locally.
Initially the industry appears to have used a multitude of small bloomeries, probably initially created by the
indigenous celts to make iron pigs(bars) which were processed locally to make weapons and tools.
The Roman shipped the iron pigs across to the Fleet headquarters at Boulogne in Gaul, probably via Portus Lemanis
the harbour near to modern Hythe, or Pevensey.
Shipbuilding
To carry the iron to Gaul required large numbers of strong cargo vessels, which could be easily made from the Oak
trees that were numerous in the Weald which bordered the sea along the coast from Pevensey to Appledore, this together
with the local iron production made transport very local and efficient. This shipbuilding would have been controlled by
Classis Britannica as part of their responsibilities.
| | |
|---|
| Main iron production period AD43 to AD290 ▲ |
|---|
Iron production and logistics
The fleet appears to have been an intrinsic part of the Roman period Wealden Iron industry, evidenced by the stamped
tiles found locally.
Initially the industry appears to have used a multitude of small bloomeries, probably initially created by the
indigenous celts to make iron pigs(bars) which were hammered into shape.
The iron produced in the Rother valley was shipped across to the Fleet headquarters at Boulogne in Gaul, probably
via Portus Lemanis the harbour near to modern Hythe. The iron produced in the Brede,Tillingham and Combe haven valleys
were probably shipped from the Pevensey area.
To carry the iron required large numbers of strong cargo vessels, which could be easily made from the Oak trees that
were numerous in the Weald and which could be easily accessed via the Pevensey level, the Combe valley and the Rother.
The trees bordering the Brede and Tillingham valleys were much more likely to have been used for charcoal production
due to the proximity of the large later production sites which required vast amounts of fuel.
During this time the Rother/Limen would have reached the sea at modern Hythe about 20 miles away from its current
mouth at Rye.
For further details on the Roman Empire Iron Production click this link Roman Iron Producing
Regions and Production
|
Production period AD43 to AD100 ▲
|
|---|
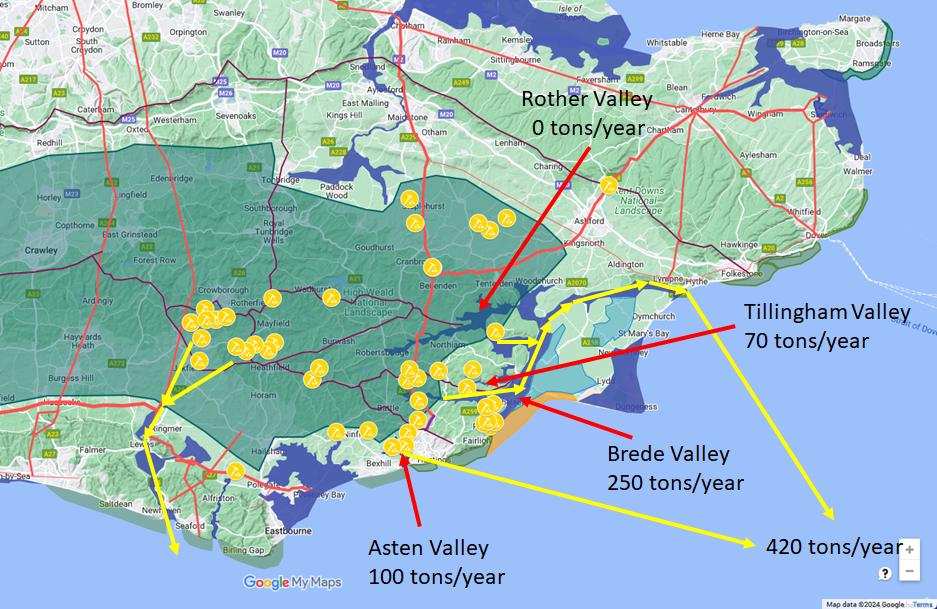 The iron was created from many small bloomeries in a similar way the the Celts originally used.
The iron was created from many small bloomeries in a similar way the the Celts originally used.
The main production came from the Brede valley with about 250 tons per year, the Asten valley produced about 100
tons and the Tillingham valley 70 tons.
Overall about 420 tons of iron was created every year from the Wealden bloomeries, and the Classis Britannica
transported this across to Bologne for processing and turning into weapons, armour and implements.
The proxiity to the forest of Andredsweald made shipbuilding as important as the iron production.
| | |
|---|
Production period AD101 to AD200 ▲
|
|---|
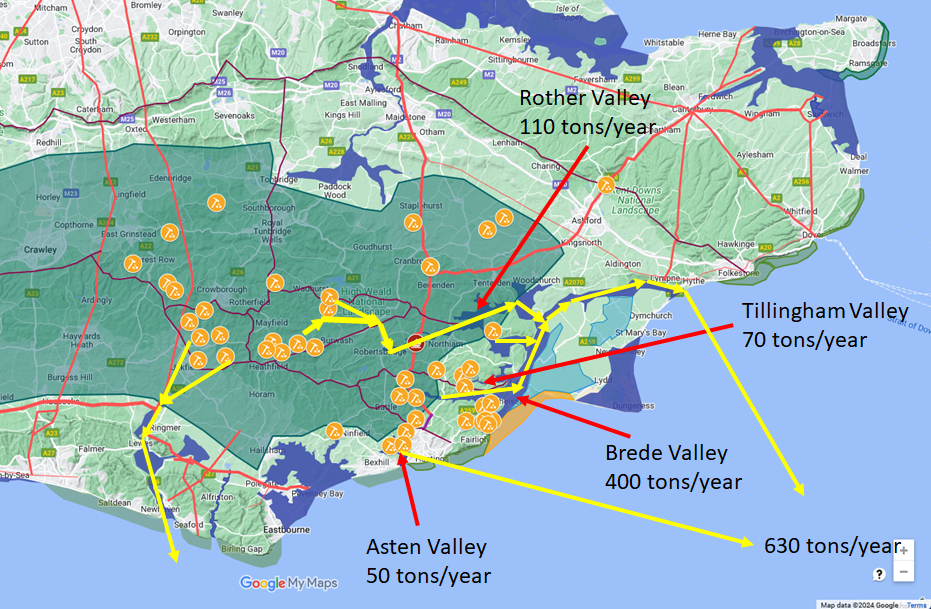 The iron is now being processed in smaller more concentrated areas and production is being ramped up.
The iron is now being processed in smaller more concentrated areas and production is being ramped up.
The main production came from the Brede valley with about 400 tons per year, the Asten valley is down to 50 tons and
the Tillingham valley remained at 70 tons, however the Rother vally is now producing 110 tons per year, with its main
port being at Bodiam where a Roman port has been discovered.
Overall about 630 tons of iron was created every year from the Wealden bloomeries, and still the Classis Britannica
transported this across to Bologne for processing and turning into weapons, armour and implements.
The probability is that more ships were being built on the Rother near Bodiam.
| | |
|---|
Production period AD201 to AD300 ▲
|
|---|
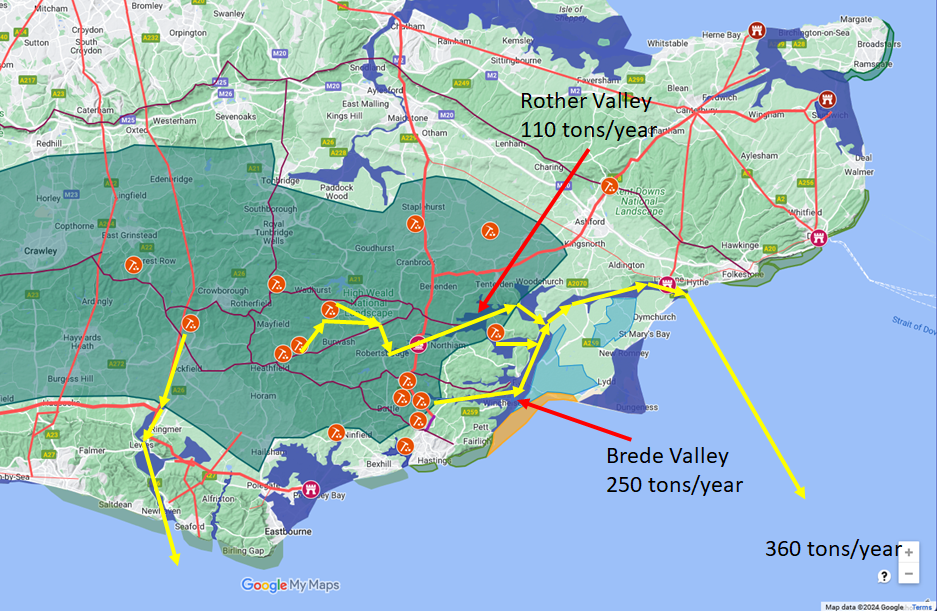 The production is now completely industrialised and coming from a few much larger production sites which are about 200
metres square such as Bardown at Stonegate, Beauport Park near Battle, Oaklands and Footlands near Sedlescombe.
The production is now completely industrialised and coming from a few much larger production sites which are about 200
metres square such as Bardown at Stonegate, Beauport Park near Battle, Oaklands and Footlands near Sedlescombe.
Overall the total iron production was down on the previous century to 360 tons however this was most likely due to
the breakaway smaller Gallic empire founded in AD260 by Postumus needing less weapons and iron implements.
And also to Carausius's declaration of independence from Rome in AD286 and the foundation of his smaller empire that
covered Britannia and northern Gaul.
The above two declarations of independence would also have required more people to build the majority of the 'Saxon
Shore Forts' built during the period which would have taken some of the labour force to use during their construction as
it would seem that Classis Britannica were in control of the construction.
|
Production period AD301 to AD400 ▲
|
|---|
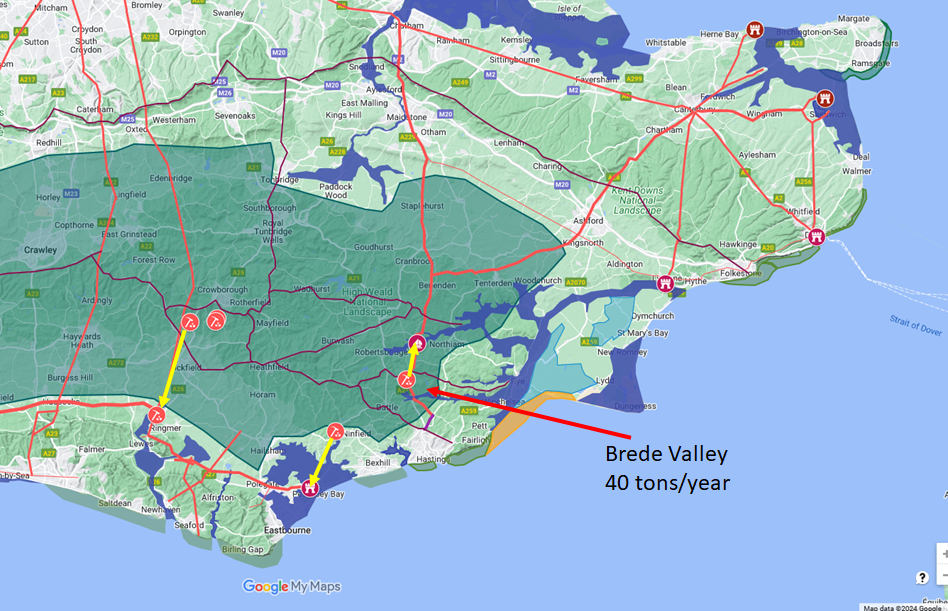 The production of iron is now down to very small volumes from the Brede valley and near modern Ashburnham to the north
of the current Pevensey marshes only amounting to about 40 tons per year, a significant drop on the previous century.
The production of iron is now down to very small volumes from the Brede valley and near modern Ashburnham to the north
of the current Pevensey marshes only amounting to about 40 tons per year, a significant drop on the previous century.
The probability is that the iron production was moved away from the Weald to other parts of the Empire nearer to
Rome such as Iberia and Austria to try to isolate the Navy and shipping from the iron working.
From this map it would seem likely that the area around Barcombe Mills was a Roman shipyard, and major port.
| | |
|---|
| Conclusion ▲ |
|---|
It would be reasonable to assume that the reduction in production was a deliberate act by the
Emperors to isolate shipbuilding from iron production because it meant that one person controlling Britannia could
easily revolt from Rome as they would control both the iron working(for weapons) and the shipbuilding(for both transport
and naval vessels) both of major importance to the empire.
Because of the intrinsic importance of shipping to the Roman Empire it would be reasonable to assume that after the 3rd
Century revolts, that the Weald would have reverted to shipbuilding and that the Classis Britannica was disbanded as an
organisation due to its potential misuse.
The small amount of iron produced in the 4th century and the areas proximity to the Forest of Anderida would be
consistent with the production of ships.
Further details about the Wealden Iron Industry can be found on the Wealden Iron Research Group Website
For our article on Iron production across the Roman Empire click the following link Roman Iron Producing
Regions and Production
| | Further Reading ▲ |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Local Interest
Just click an image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|